利用DESeq2包进行差异表达分析。
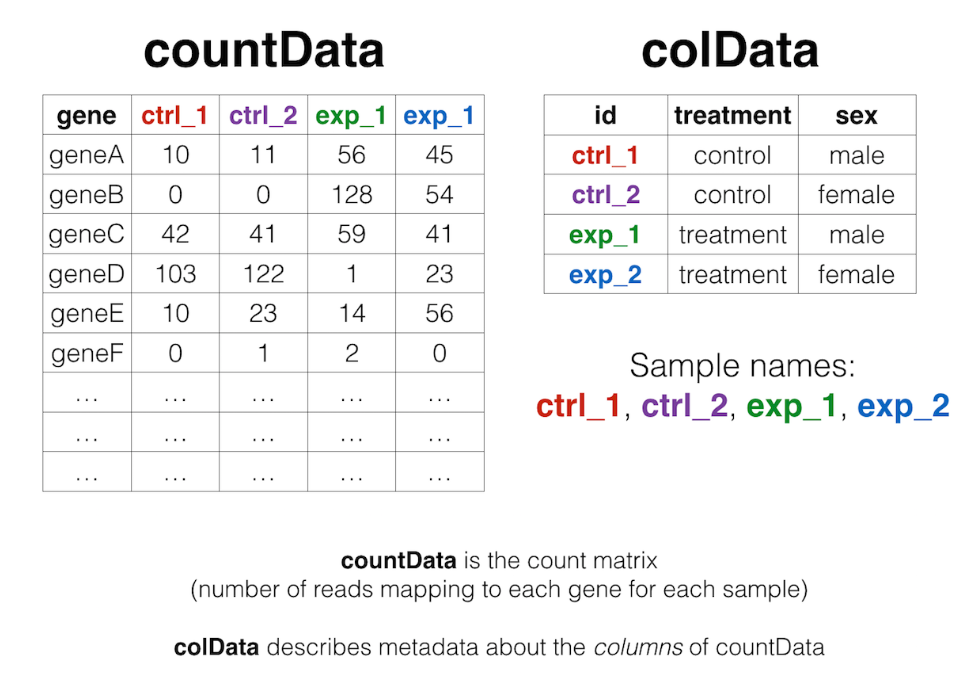
1. 读入数据并构建DESeq2对象 DESeq2差异分析是使用原始counts数据进行分析的,首先要创建DESeq2包能够处理的对象,创建该对象需要三个数据集:
读入数据及预处理:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 library( DESeq2) library( dplyr) library( ggplot2) library( ggrepel) count <- read.table( file = "counts.txt" ) rownames( count) <- count$ V1 count <- count[ , 2 : 5 ] count <- count[ rowSums( count) > 0 , ] colnames( count) <- c ( "CS-1" , "CS-2" , "PS-1" , "PS-2" ) count <- count[ - 1 , ]
三个dataframe:
1 2 3 4 group_list <- rep ( c ( "CS" , "PS" ) , each = 2 ) colData <- data.frame( sample = colnames( count) , group_list = group_list )
有了这三个矩阵信息,就可以进行接下来DESeq2对象的构建了。
1 2 dds <- DESeqDataSetFromMatrix( countData = count, colData = colData, design = group_list)
2. 差异分析 接下来可以进行差异分析,并提取差异分析的结果。
1 2 3 dds2 <- DESeq( dds) res <- results( dds2, contrast= c ( "group_list" , "CS" , "PS" ) )
这里需要注意contrast参数,两个组的先后顺序如果不同分析出来的差异。原文是这样写的:
The results table when printed will provide the information about the comparison, e.g. “log2 fold change (MAP): condition treated vs untreated”, meaning that the estimates are of log2(treated / untreated), as would be returned by contrast=c(“condition”,”treated”,”untreated”).
所以两个组的顺序应该是对照在后面,实验组在前面,否则得到的上下调基因会刚好相反。
res中包含的列:base means across samples, log2 fold changes, standard errors, test statistics, p-values and adjusted p-values。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 res$ symbol <- mapIds( org.Dm.eg.db, keys= row.names( res) , column= "SYMBOL" , keytype= "ENSEMBL" , multiVals= "first" ) res$ entrez <- mapIds( org.Dm.eg.db, keys= row.names( res) , column= "ENTREZID" , keytype= "ENSEMBL" , multiVals= "first" ) res$ name = mapIds( org.Dm.eg.db, keys= row.names( res) , column= "GENENAME" , keytype= "ENSEMBL" , multiVals= "first" )
1 2 3 4 5 6 res_ordered <- res[ order( res$ pvalue) , ] DEG <- as.data.frame( res_ordered) DEG <- na.omit( DEG)
3. 根据差异表达倍数确定上下调的基因 确定上下调表达的基因,可以选择静态阈值或者动态阈值。静态阈值比如:p<0.05,logFC>2。动态阈值根据数据整体的情况确定一个阈值。
如果采用动态阈值,则计算动态阈值的代码如下:
1 2 3 logFC_t <- with( DEG, mean( abs ( log2FoldChange) ) + 2 * sd( abs ( log2FoldChange) ) ) logFC_t <- round ( logFC_t, 2 )
这里以采用静态阈值2为例进行分析并绘制火山图,也可以采用padj确定上下调基因。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 DEG$ change = as.factor( ifelse( DEG$ pvalue < 0.05 & abs ( DEG$ log2FoldChange) > 2 , ifelse( DEG$ log2FoldChange > 2 , 'UP' , 'DOWN' ) , 'STABLE' ) ) table( DEG$ change) DEG$ label <- ifelse( DEG$ pvalue < 0.00000001 & abs ( DEG$ log2FoldChange) >= 3 , DEG$ symbol, "" ) ggplot( DEG, aes( x= log2FoldChange, y= - log10( pvalue) , color= change) ) + geom_point( alpha= 0.4 , size= 2 ) + theme_classic( ) + xlab( "log2 fold change" ) + ylab( "-log10 pvalue" ) + theme( plot.title = element_text( size= 15 , hjust = 0.5 ) ) + scale_colour_manual( values = c ( 'blue' , 'black' , 'red' ) ) + geom_hline( yintercept = - log10( 0.05 ) , lty = 2 ) + geom_vline( xintercept = c ( - 2 , 2 ) , lty = 2 ) + geom_label_repel( data = DEG, aes( label = label) , size = 3 , box.padding = unit( 0.5 , "lines" ) , point.padding = unit( 0.8 , "lines" ) , segment.color = "black" , show.legend = FALSE , max.overlaps = 10000 )
到这里,差异分析就完成啦!
参考链接:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/694b40961fc7 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzUzMTEwODk0Ng==&mid=2247497831&idx=1&sn=5fc90f8b4a3d0955566a869bed164cee&chksm=fa453d5acd32b44c05eb25fbecda756d82b9aa052149995b437d58088582aaf44e8287907c63&scene=178&cur_album_id=1749887454125293572#rd